Carbureted vs fuel-injected bikes: What's the difference?
Are fuel injectors always better than carburetors?
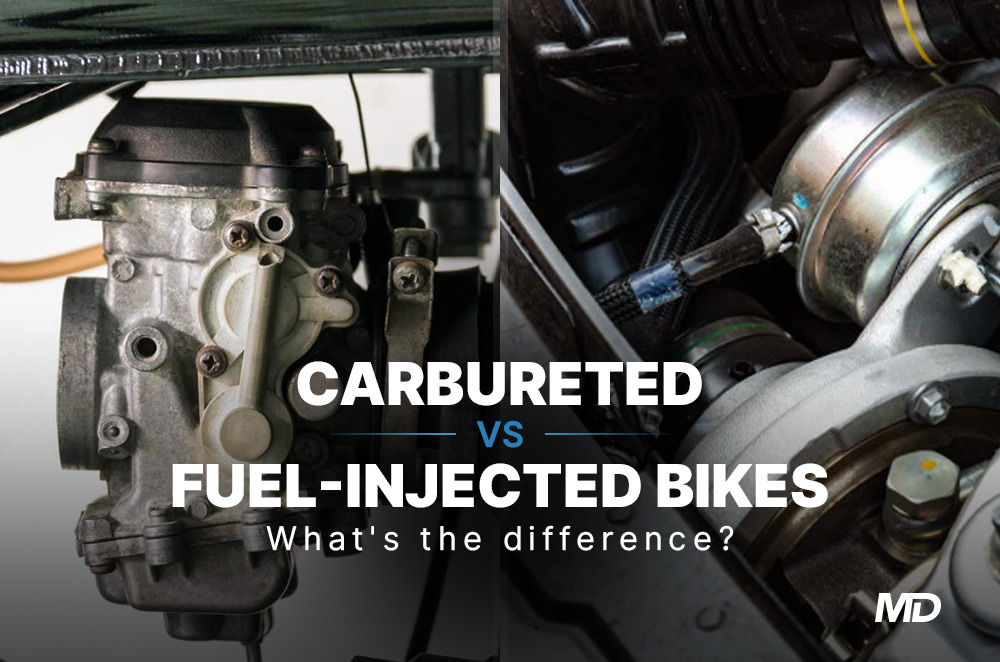
Fuel-injected motorcycles are everywhere nowadays. They're in everything from maxi-scooters to high-end naked bikes and performance sportbikes. While fuel injection (FI) has become the norm for engine design for quite some time, carbureted engines still have a place in the motoring world.
Carburetors are reliable and simple in design. This makes them easier to tinker with and fix. They can also still keep up in terms of performance. In fact, some well-tuned carbureted bikes can still go toe-to-toe with today's best motorcycles. That said, what's the difference between carbureted and fuel-injected bikes?
What is a motorcycle carburetor?

Before fuel injection, a carb was the only way for a motorcycle engine to achieve the necessary air and fuel ratio. Due to this, carbs dominated the motoring landscape.
Put simply, carburetors work using an intake vacuum to force the piston to draw fuel up and into the combustion chamber. The amount of air is then decided by a throttle valve connected to the cylinder. This makes it that the engine produces more power as you pull on the throttle. It's important to note that this process is entirely mechanical in most carbureted engines and doesn't rely on electronic parts. This mechanical makeup is partly why carbs have earned a reputation for being simple to repair and modify. However, carburetors can also have a slightly slower throttle response due to the inexact fuel ratio that they produce.
Carburetors have faded in recent years, but they can still be found in many motorcycles locally. Due to their penchant for pollution, carbs have seen limited use in mostly scooters and entry-level bikes. That said, carburetors still have some positive points on their side. You can tune a carb easily with a few specific tools, and since it's not connected directly to the motor, you can access it without touching the engine block.
What is a fuel-injected motorcycle?

While fuel injection had been present as early as the 1930s, it wasn't until the 1980s when the technology made its way into bikes. This was the time when electronic fuel injection (EFI) became available. Unlike the mechanical components of carbs, EFI systems feature a computerized engine control unit (ECU) that automatically calculates the ideal air to fuel ratio.
A fuel-injected system depends on a fuel pump to carry and control the flow of fuel. The fuel is then heated and atomized in specific temperatures to ensure a cleaner burn and fewer fuel emissions.
Due to their efficiency, fuel-injected engines have largely replaced carburetors in modern vehicles. Their advantages include a sharper throttle response, significantly lower maintenance costs, and slightly better power and fuel economy. Fuel-injected systems are also resilient and generally require little maintenance.
For all their differences, carburetors and fuel injectors both serve the same purpose. That is to ensure an optimal level of air and fuel mixture to generate combustion. While fuel injection is a more advanced technology, this doesn't mean that carburetors have lost their place in the industry. Carbs can still do the job they're meant to do, just not as efficiently and reliably as fuel injectors. On the other hand, carbs are more affordable and simpler to repair. Both can be good options depending on what you’re looking for.
Related Articles
-
Motorcycle 101: what exactly does “cc” in a motorcycle mean? / Featured Article
Beginner riders often ask us what the term “cc” refers to in the world of motorcycles. Read on to learn more about this vital and ubiquitous term.
-
What engine configuration is best for middleweight street bikes? / Featured Article
Modern street bikes come in all sorts of engine configurations. Read on to find out which is best for your riding style.
-
Parallel-twin or V-twin - Which should you choose? / Featured Article
Read on to learn more about two of the most popular engine configurations for big bikes, and which one you should choose.
-
Will engine braking damage your motorcycle’s engine? / Tips & Advice
It’s a common misconception that engine braking will damage your engine. Let’s debunk this myth once and for all.
-
What is a rev limiter and what does it do? / Featured Article
Why do all modern motorcycle engines have a rev limiter? What is it for and why does it sound the way it does? Read on to learn more.
Latest Features
-
Last-minute Christmas gift ideas for your rider friends and family / Featured Article
Struggling to think of gift ideas for your motorcyclist friends and family? Read on to get some inspiration this gift-giving season.
-
Ride a naked sportbike? Get these 5 upgrades first / Featured Article
Here’s a quick list of 5 upgrades to your naked sportbike to enhance your riding experience.
-
Motorcycle 101: The inner workings of a slipper clutch / Featured Article
Slipper clutches are awesome as they make for more forgiving downshifts and a lighter clutch lever. Let’s take a closer look at them and see how they work.








